Earwax Removal
What is earwax?
Earwax is a yellowish, waxy substance that originates in the ear canal. Comprised of oils, sweat, and dead skin cells, glands inside the ear produce earwax. This wax can be either wet or dry, depending on its composition. Earwax helps to maintain optimal conditions within the ear canal. Occasionally, earwax can accumulate in the ear canal, leading to hearing loss, pain, or other issues. Cleaning out the excess earwax may be necessary to restore normal hearing and alleviate pain.
Are there different types of earwax?
Your type of earwax could be determined by your DNA!
There are two main types of earwax: wet and dry. Wet earwax is typically produced in people of African, Native American, and East Asian descent and is softer and more yellow or brown. Dry earwax is generally made in people of European descent and is drier and lighter in color.
Genetics determines the type of earwax a person will have.
DNA research identified the gene ABCC11 as the primary genetic factor in determining whether a person will produce wet or dry earwax.
While there is no direct relationship between earwax and DNA research, the study of genetics can provide insights into the factors that influence the production and characteristics of earwax and other physical traits and characteristics. Earwax can become impacted or blocked when it cannot independently move out of the ear canal. Impacted earwax can happen when it becomes too hard or is pushed further into the ear canal using cotton swabs, fingers, or other objects inserted into the ear.
What Causes Impacted Earwax?
Earwax can become impacted or blocked when it cannot move out of the ear canal on its own. Impacted earwax can happen when it becomes too hard or is pushed further into the ear canal by using cotton swabs, fingers, or other objects inserted into the ear.
Impacted earwax can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
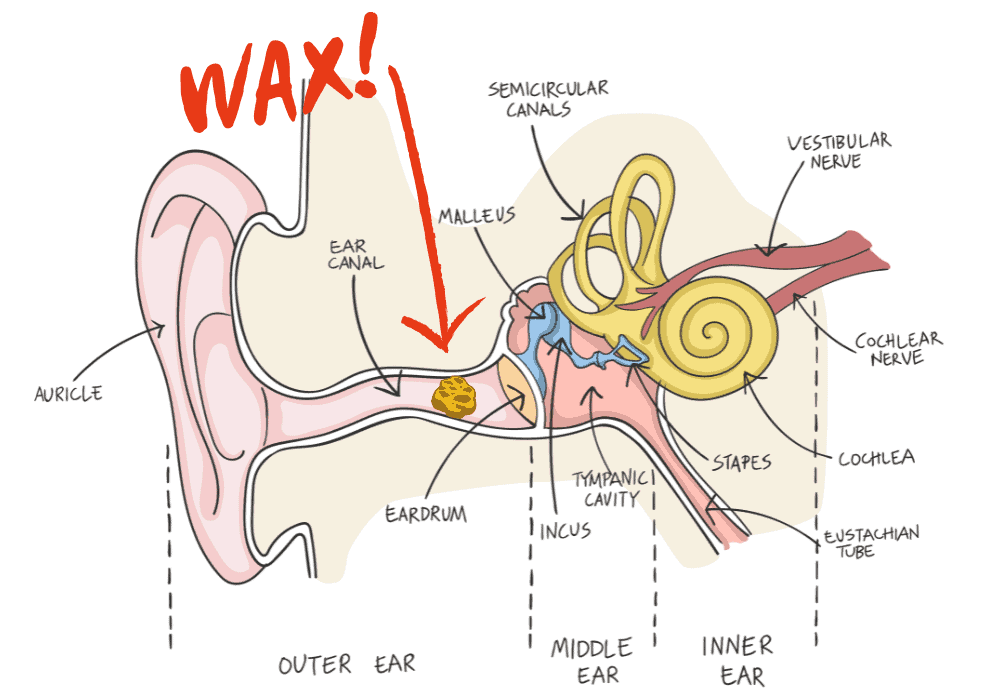
- Earache: Impacted earwax can press against the ear drum and cause pain or discomfort.
- Hearing loss: Earwax that is blocking the ear canal can partially or completely obstruct sound waves from reaching the ear drum, causing temporary hearing loss.
- Ringing in the ear: Impacted earwax can cause a sensation of ringing, buzzing, or other noises in the ear, known as tinnitus.
- Fullness in the ear: The presence of impacted earwax can give the feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
- Discharge: In some cases, impacted earwax can cause a discharge from the ear, which may be accompanied by an unpleasant smell.
How is Earwax Removed?
There are several traditional methods for removing earwax.
Earwax removal is beneficial in certain situations by alleviating symptoms such as hearing loss, earache, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Ear irrigation is a standard method for removing earwax. A healthcare provider will use a small, curved instrument to gently flush the ear canal with water or a saline solution.
Additionally, a healthcare provider may gently use forceps or other tools to remove the earwax from the ear canal. One can also try ear drops containing hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, which loosens the ear wax for easier removal.
Is there an easier way to remove Earwax?
Absolutely!
Yes! The professional at Active Life Hearing, use the Earigator™ technology to remove even the most stubborn ear wax effortlessly and securely. Utilizing this advanced system makes keeping your ears clean a simple task!
This effective wax removal process is just as impressive as its name implies.
Potential benefits of removing impacted earwax include:
- Improved hearing: Excess earwax can block the ear canal and cause hearing loss. Removing the earwax can restore normal hearing.
- Relief from earache: Earwax can sometimes cause earache if it becomes impacted in the ear canal. Removing the earwax can provide relief from this type of pain.
- Prevention of ear infections: Earwax helps to keep the ear canal clean and healthy by trapping dirt, dust, and other foreign substances. However, if earwax builds up excessively, it can create a breeding ground for bacteria and increase the risk of ear infections. Removing earwax can help to prevent these types of infections.
Just Say No To The Q-Tip
Inserting a Q-tip or other object into the ear can push wax and debris further into the ear canal, potentially causing blockages or impaction. This can lead to earache, temporary hearing loss, or damage to the eardrum. Using Q-tips can also irritate the skin inside the ear canal, potentially leading to infection.
Contact Active Life Hearing today to have your ears checked for impacted wax. Click Below
Thank you, our staff will reach out shortly
Our Patients say it best



Our Patients Say It Best




