Impacted Earwax
What It Is and How to Deal With It
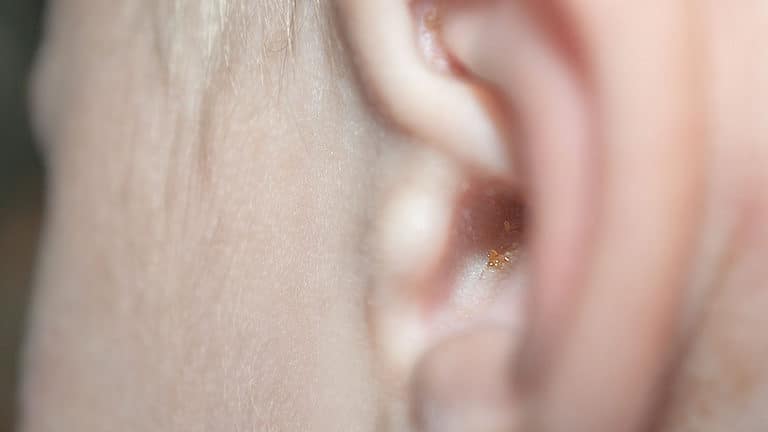
Earwax, technically “cerumen,” is a natural substance produced by the body to protect the ear canal and keep it clean. Sometimes earwax can become impacted, causing a variety of symptoms and complications. In this blog post, we’ll explore what impacted earwax is, how it develops, and how you can deal with it.
What is impacted earwax?
How does earwax become impacted?
What are the symptoms of Impacted Earwax
- Earache
- Itching in the ear
- Decreased hearing or muffled hearing
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
- Dizziness
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
How does earwax become impacted?
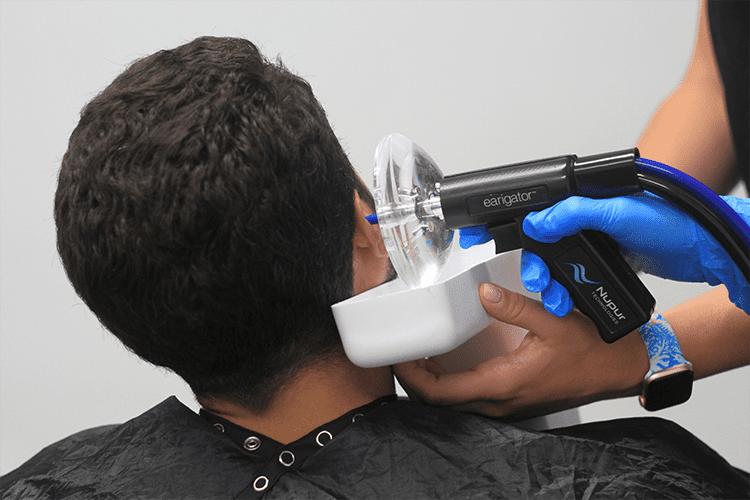
At Active Life Hearing, our professionals are trained in earwax removal with the Earigator™. The Earigator™ allows us to perform cerumen removal safely and efficiently.
Designed by an Otologist, the EarigatorTM combines the functions of an otoscope and irrigation into one, providing the most advanced means of earwax removal.
With the EarigatorTM, nurses and clinicians can safely and efficiently remove even the most stubborn ear wax.
Self-contained temperature control regulates the water to body temperature, avoiding any caloric or vertigo side effects.
Pressure controls ensure that the EarigatorTM quickly removes even impacted earwax while never endangering the eardrum.

An Erigator™ treatment in progress