History Of Hearing Aids
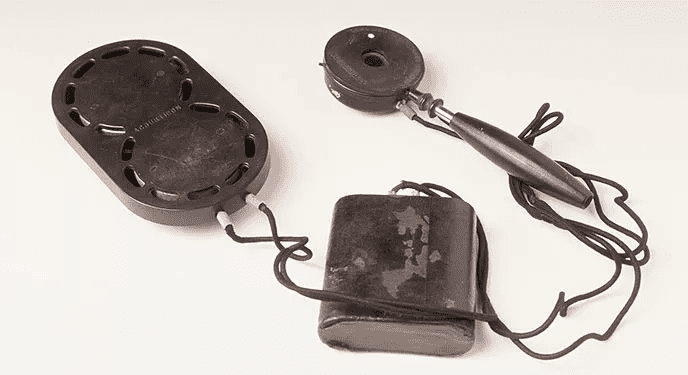
Hearing aids have been around for centuries, but it wasn’t until the 20th century that they began to resemble the modern devices we use today. The first electric hearing aid was invented in the 1890s, but it needed to be more light and practical.
In the 1920s, vacuum tube technology allowed for smaller, more powerful hearing aids. In the 1950s, transistor technology made hearing aids even smaller and more reliable in the 1980s, digital signal processing technology allowed for more precise customization of hearing aids for individual hearing loss.
Today’s hearing aids are small, discreet, and highly effective, with many advanced features such as Bluetooth connectivity, rechargeable batteries, and artificial intelligence for noise reduction and speech enhancement.
Hearing Aid Manufacturers
There are five major manufacturers of hearing aids world wide. They focus the majority of hearing aid research and development on mild-to-severe hearing. Here is a brief description of some of the largest and most well-known companies.
- Phonak: Phonak is a Swiss-based company that has been in business for over 70 years. They produce hearing aids for people with mild to severe hearing loss. Phonak was the first to introduce digital hearing aids in the early 1990s. They continue to innovate with advanced features such as rechargeable batteries, Bluetooth connectivity, and AI-powered noise reduction.
- Signia: Signia was formerly known as Siemens Hearing Instruments before being acquired by the Sivantos Group in 2015. Signia is known for its focus on cutting-edge technology, such as its Nx platform, which uses AI to adjust automatically to different listening environments.
- Widex: Widex is a Danish company that has been in business for over 60 years. They are known for their focus on sound quality and their use of their proprietary Zen sound therapy, which aims to reduce tinnitus symptoms. Widex was purchased in a merger with Sivantos in March 2019. The new company is known as WS audiology
- Oticon: Oticon is a Danish company that has been in business for over 100 years. They were the first company to introduce a digital hearing aid in 1995. Oticon hearing aids use BrainHearing technology, which focuses on how the brain processes sound.
- Starkey: Starkey is an American company that has been in business for over 50 years. They are known for their focus on customization and personalization, with hearing aids tailored to an individual’s specific hearing needs. Starkey was the first company to introduce a hearing aid controlled by a smartphone app.
Benefits of Hearing Aids
Improved communication and quality of life
Hearing aids can transform the lives of people with hearing loss, improving their communication abilities and overall quality of life. For those with hearing loss, hearing aids can be essential for staying engaged and connected with the world around them.
By amplifying sounds and making them clearer, hearing aids can help individuals better understand speech, particularly in noisy environments. This can be a game-changer for those who need help to keep up with conversations or feel left out of social situations. Improved hearing ability can restore social interactions, allowing people to maintain relationships and avoid the feelings of isolation and loneliness that can come with hearing loss.
Hearing aids can also help reduce the fatigue and stress of straining to hear and understand speech. With hearing aids, people can enjoy more activities without feeling exhausted or overwhelmed. Additionally, hearing aids can increase safety by allowing people to better hear warning signals, traffic noise, and other environmental sounds.
Untreated hearing loss has been linked to cognitive decline and dementia. Still, hearing aids can help preserve cognitive function and maintain brain health. People can stay engaged with the world around them with better hearing and maintain an active and healthy lifestyle.
By improving communication, social interactions, safety, and overall well-being, hearing aids can help people stay engaged and connected with the world around them.
Enhanced cognitive function and brain health
Hearing aids are not only essential for improved communication, but they can also provide cognitive benefits that improve brain function and overall health. For people with hearing loss, hearing aids can help reduce the cognitive load associated with straining to hear. By reducing the effort required to listen, hearing aids can free up mental resources, allowing people to devote more attention to other tasks, such as memory and learning.
Hearing aids also provide an essential source of brain stimulation. When people with hearing loss receive less auditory input, it can reduce brain activity and efficiency. By providing the brain with the auditory information it needs, hearing aids can help improve brain function and maintain healthy brain activity.
In addition to providing cognitive benefits, hearing aids can also help prevent social isolation and depression, which can negatively impact cognitive health. Hearing loss is associated with an increased risk of social isolation and depression, which can lead to cognitive decline. By improving communication and social interaction, hearing aids can help prevent the negative impact of social isolation on mental health.
Research also suggests that untreated hearing loss may lead to changes in brain structure, such as a reduction in gray matter volume. Using hearing aids can help preserve brain structure and maintain cognitive function. Furthermore, hearing aids can help reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Hearing loss is a well-established risk factor for cognitive decline. By improving hearing ability, hearing aids may help reduce this risk and preserve cognitive function in the long term.
Hearing aids can provide numerous cognitive benefits for people with hearing loss. By reducing cognitive load, improving brain stimulation, preventing social isolation, preserving brain structure, and reducing the risk of cognitive decline, hearing aids can help support healthy cognitive aging and improve overall brain function and health.
Reduced risk of depression and anxiety
Hearing aids can help reduce the risk of depression and anxiety for people with hearing loss. When people with hearing loss struggle to communicate, they can feel isolated and disconnected from the world around them, which can lead to feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression. However, hearing aids can help alleviate these negative emotions in several ways.
Firstly, hearing aids can improve communication ability, allowing people to participate more fully in social interactions. When people can hear and understand speech more clearly, they can better engage in conversations and feel more connected with others. This can help reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can contribute to depression and anxiety.
Secondly, hearing aids can improve overall quality of life, making it easier for people with hearing loss to enjoy everyday activities. By improving hearing ability, hearing aids can allow people to engage in hobbies, attend events, and participate in daily life with more ease and enjoyment. This can help prevent feelings of sadness or hopelessness that can lead to depression.
Thirdly, hearing aids can reduce cognitive load, which can help alleviate anxiety. When people with hearing loss strain to hear, they devote more cognitive resources to the effort of listening. This can lead to mental exhaustion and cognitive overload, making it difficult to concentrate and focus. By reducing the cognitive load of listening, hearing aids can help alleviate stress and anxiety and provide a greater sense of ease and comfort.
Hearing aids can reduce the risk of depression and anxiety for people with hearing loss by improving communication ability, enhancing overall quality of life, and reducing cognitive load. By allowing people to engage in daily activities with more ease and enjoyment, hearing aids can help support mental health and well-being.
Increased safety and awareness in social and public settings

Wearing hearing aids can increase safety and awareness for people with hearing loss in social and public settings in several ways. People with hearing loss may struggle to hear warning signals, traffic noise, or other environmental sounds, putting them at risk of accidents or injury.
Hearing aids can help improve hearing ability, allowing people to better perceive sounds in their surroundings and stay safe. For example, when crossing the street, people with hearing loss may not hear approaching vehicles, increasing their risk of being hit by a car. By using hearing aids, they can better hear traffic noise and safely navigate their environment.
In social settings, hearing aids can help people stay aware of their surroundings and follow social cues. People with hearing loss may struggle to hear announcements or instructions in public places, such as airports, train stations, or shopping malls. Hearing aids can help them hear important information and stay informed of environmental changes.
Hearing aids can also help people with hearing loss stay aware of potential hazards, such as fire alarms or emergency announcements. By better perceiving sounds in their environment, people can respond quickly to emergencies and stay safe.
In addition to improving safety, hearing aids can also help people with hearing loss feel more confident and at ease in social and public settings. By reducing the effort required to hear and understand speech, hearing aids can help people feel more engaged and included in conversations, leading to increased confidence and social connections.
Hearing aids can significantly increase safety and awareness for people with hearing loss in social and public settings. By improving hearing ability, hearing aids can help people better perceive sounds in their environment and stay safe. Furthermore, by increasing confidence and social connections, hearing aids can help people feel more at ease and comfortable in various situations.
Demographics of Hearing Aid Users
The demographics of hearing aid users vary by geography, age, sex, and income level. According to a report by the World Health Organization, an estimated 466 million people worldwide have disabling hearing loss, with prevalence rates highest in low- and middle-income countries. However, hearing loss affects people of all ages and demographics.
In the United States, approximately 15% of adults (37.5 million) report hearing loss. Prevalence rates increase with age, with over half of adults aged 75 and older experiencing hearing loss. Men are more likely than women to have hearing loss, and rates of hearing loss are higher among non-Hispanic white adults than among other racial and ethnic groups.
Regarding income, research suggests that individuals with lower socioeconomic status are less likely to use hearing aids. Cost is a significant barrier to hearing aid use, with many people unable to afford the high cost of hearing aids and related services. This can limit access to care and lead to untreated hearing loss.
In many countries, including the United States, hearing aid use remains low among people with hearing loss. According to a study published in JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, only 14% of adults with hearing loss in the United States use hearing aids. This may be partly due to a lack of awareness about the benefits of hearing aids and the importance of seeking care for hearing loss.
The demographics of hearing aid users reflect the widespread prevalence of hearing loss across all ages, sexes, and income levels. However, access to care and affordability remain significant barriers to hearing aid use, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Efforts to improve awareness, affordability and access to hearing healthcare are needed to ensure that all individuals with hearing loss can benefit from hearing aids.
Factors that influence hearing aid adoption rates
- Cost: The high cost of hearing aids is a significant barrier for many people, particularly those with lower incomes or without insurance coverage.
- Stigma: Despite the prevalence of hearing loss, a social stigma is still associated with hearing aids. Some people may be reluctant to wear hearing aids due to concerns about how others will perceive them.
- Lack of awareness: Many people with hearing loss are not aware of the benefits of hearing aids or may not realize that they have hearing loss.
- Denial: Some people may be in denial about their hearing loss or may not want to acknowledge that they need hearing aids.
- Fear of technology: Hearing aids are becoming increasingly technologically advanced, which can be intimidating for some people, particularly older adults.
- Lack of access to care: In many areas, there may be a shortage of hearing healthcare providers, making it difficult for people to access care.
- Lack of insurance coverage: While some insurance plans cover the cost of hearing aids, many do not, making them unaffordable for many people.
- Poor fit or comfort: Some people may try hearing aids and find them uncomfortable or poorly fitting, leading to discontinuation of use.
- Mismatched expectations: Some people may have unrealistic expectations about what hearing aids can do or may be disappointed with their performance.
- Lack of follow-up care: Follow-up care and adjustments to hearing aids are essential for optimal performance, but some people may not receive the necessary maintenance or may not follow through with recommended appointments
Technology in Hearing Aids
The evolution of hearing aid technology has been a gradual process of refinement and innovation, with each breakthrough building on past successes. From the first crude trumpet-shaped devices of the late 19th century to the sophisticated digital hearing aids of today, numerous breakthroughs, companies, and dates have helped transform the industry.
Early hearing aids were simple devices that amplified sound using mechanical means, such as a horn or a wooden resonator. Although large and unwieldy, these devices were a significant breakthrough in helping people with hearing loss.
The development of carbon microphones in the 1920s enabled the creation of smaller, more practical hearing aids. Carbon microphones convert sound waves into electrical signals that are amplified and transmitted to the ear.
Vacuum tubes were introduced in the 1940s, allowing for greater amplification and more compact devices. This technology enabled the development of behind-the-ear (BTE) and in-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids.
The invention of the transistor in the 1950s revolutionized the hearing aid industry. Transistors were smaller, more reliable, and more energy-efficient than vacuum tubes, which made hearing aids even more compact and portable. This technology enabled the development of in-the-canal (ITC) and completely in-the-canal (CIC) hearing aids.
In the 1990s, digital signal processing (DSP) technology was introduced, allowing for more significant sound processing and programming precision. DSP enabled hearing aids to be programmed to the specific needs of each individual user. It also made it possible to incorporate additional features, such as noise reduction and directional microphones.
The introduction of wireless connectivity in the 2000s was a significant breakthrough in hearing aid technology. This wireless connectivity allows hearing aids to communicate with other devices, such as smartphones, televisions, and music players, improving the listening experience and providing greater convenience for users.
Some major companies that have contributed to the evolution of hearing aid technology include Siemens, Phonak, Oticon, Widex, and Starkey. These companies have been at the forefront of innovation. They have helped to drive the development of new and better technologies for people with hearing loss.
The evolution of hearing aid technology has been gradual refinement and innovation, resulting in smaller, more energy-efficient devices with greater precision and advanced features. These advancements have greatly improved the quality of life for people with hearing loss, and there is much optimism for continued innovation in this field.
AI advancements in hearing aid technology

Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly impacted hearing aid technology in recent years. AI has been incorporated into hearing aids to help improve sound quality, reduce background noise, and provide a more personalized listening experience. Here are some of the ways that AI has impacted hearing aid technology:
- Noise reduction: AI-powered hearing aids use machine learning algorithms to recognize and reduce background noise in real time. This allows the user to focus on the sounds they want to hear, making it easier to understand speech and engage in conversations.
- Personalization: AI-powered hearing aids can be programmed to the individual needs of the user, taking into account their hearing loss, lifestyle, and preferences. This allows for a more customized listening experience tailored to the user’s specific needs.
- Automatic adjustments: AI-powered hearing aids can make automatic adjustments based on the user’s environment, such as reducing volume in quiet environments and increasing it in noisy ones. This can help provide a more seamless and comfortable listening experience.
- Enhanced sound quality: AI-powered hearing aids can improve sound quality, allowing for clearer and more natural sound. This is achieved through advanced signal processing algorithms that can help restore missing frequencies and enhance speech intelligibility.
- Connectivity: AI-powered hearing aids can connect to other devices, such as smartphones, allowing for greater control and customization. This can also enable new features, such as streaming music and phone calls directly to the hearing aids.
Overall, the impact of AI on hearing aid technology has been significant, helping to improve sound quality, reduce background noise, and provide a more personalized and comfortable listening experience. As AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements and advancements in hearing aid technology that will benefit people with hearing loss.
Conclusion
Hearing aids have come a long way since their inception, with the evolution of technology allowing for smaller, more efficient, and more effective devices. Despite the benefits of hearing aids, many people with hearing loss are still reluctant to use them due to stigma, cost, or other barriers. However, with the continued advancements in technology, such as AI, we can expect to see even more improvements in hearing aid functionality and accessibility in the future. The impact of hearing aids on communication, cognitive function, and quality of life for people with hearing loss is significant, making it an important tool for improving overall health and well-being. With greater awareness and access to care, we can work towards ensuring that everyone who needs a hearing aid can benefit from this life-changing technology.




